Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world, known for its versatility, portability, and wide range of applications. Java is the most used language in top companies such as Uber, Airbnb, Google, Netflix, Instagram, Spotify, Amazon, and many more because of its features and performance.
In this article, we will provide 200+ Core Java Interview Questions tailored for both freshers and experienced professionals with 3, 5, and 8 years of experience. Here, we cover everything, including core Java concepts, Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), multithreading, exception handling, design patterns, Java Collections, and more, that will surely help you to crack Java interviews. Along with these interview questions you can also try Java course to enhance your Java concepts.
Table of Content
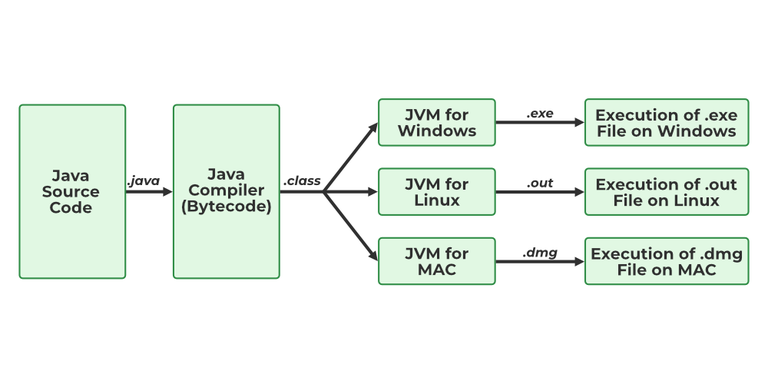
Yes, Java is a Platform Independent language. Unlike many programming languages javac compiles the program to form a bytecode or .class file. This file is independent of the software or hardware running but needs a JVM(Java Virtual Machine) file preinstalled in the operating system for further execution of the bytecode.
Although JVM is platform dependent , the bytecode can be created on any System and can be executed in any other system despite hardware or software being used which makes Java platform independent.
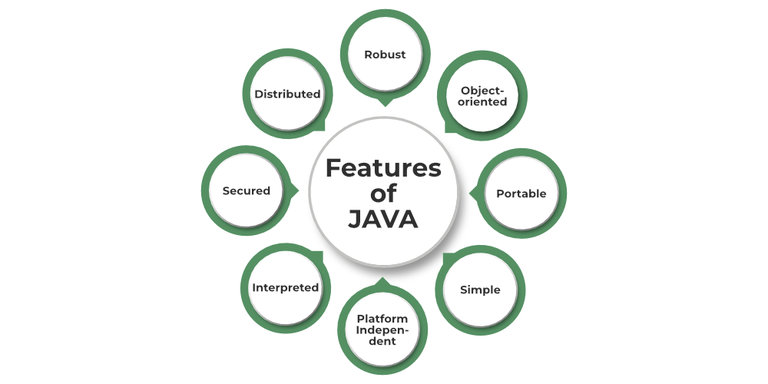
Java is one the most famous and most used language in the real world, there are many features in Java that makes it better than any other language some of them are mentioned below:

JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine it is a Java interpreter. It is responsible for loading, verifying, and executing the bytecode created in Java.
Although it is platform dependent which means the software of JVM is different for different Operating Systems it plays a vital role in making Java platform Independent.
To know more about the topic refer to JVM in Java .
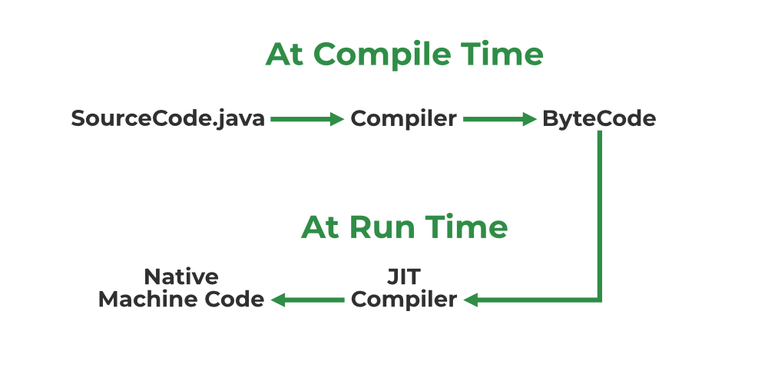
JIT stands for (Just-in-Time) compiler is a part of JRE(Java Runtime Environment), it is used for better performance of the Java applications during run-time. The use of JIT is mentioned in step by step process mentioned below:
To know more about the topic refer to JIT in Java .
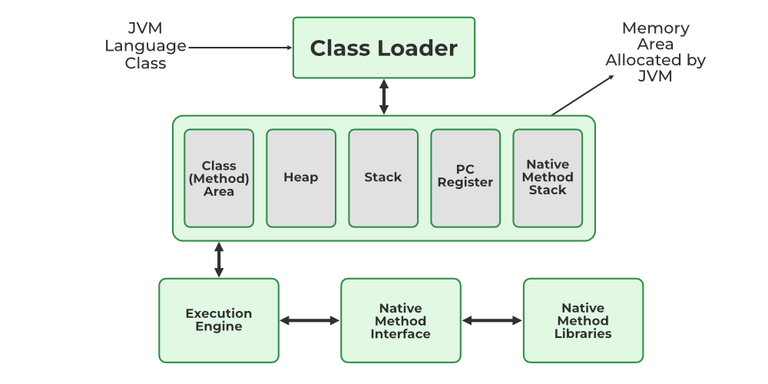
JVM consists of a few memory storages as mentioned below:
To know more about the topic refer to JVM Memory Storages .
Classloader is the part of JRE(Java Runtime Environment), during the execution of the bytecode or created .class file classloader is responsible for dynamically loading the java classes and interfaces to JVM(Java Virtual Machine). Because of classloaders Java run time system does not need to know about files and file systems.
To know more about the topic refer to ClassLoader in Java.
JVM : JVM also known as Java Virtual Machine is a part of JRE. JVM is a type of interpreter responsible for converting bytecode into machine-readable code. JVM itself is platform dependent but it interprets the bytecode which is the platform-independent reason why Java is platform-independent.
JRE : JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment, it is an installation package that provides an environment to run the Java program or application on any machine.
JDK : JDK stands for Java Development Kit which provides the environment to develop and execute Java programs. JDK is a package that includes two things Development Tools to provide an environment to develop your Java programs and, JRE to execute Java programs or applications.
To know more about the topic refer to the Differences between JVM, JRE, and JDK .
C++ is Platform Dependent
Java is Platform Independent
C++ is mainly used for System Programming
Java is Mainly used for Application Programming
C++ is nearer to hardware
Java is not so interactive with hardware
C++ supports global and namespace scope.
Java doesn’t support global scope.
Functionality supported in Java but not in C++ are:
Functionality supported in C++ but not in Java are:
C++ is an object-oriented language. It is not a single root hierarchy .
Java is also an object-oriented language. It is a single root hierarchy as everything gets derived from a single class (java.lang.Object).
C++ always creates a new inheritance tree.
Java uses a Single inheritance tree as classes in Java are the child of object classes in Java.
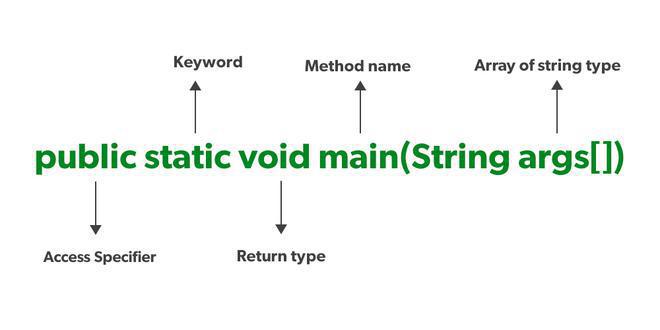
Unlike any other programming language like C, C++, etc. In Java, we declared the main function as a public static void main (String args[]). The meanings of the terms are mentioned below:
A Java String Pool is a place in heap memory where all the strings defined in the program are stored. A separate place in a stack is there where the variable storing the string is stored. Whenever we create a new string object, JVM checks for the presence of the object in the String pool, If String is available in the pool, the same object reference is shared with the variable, else a new object is created.
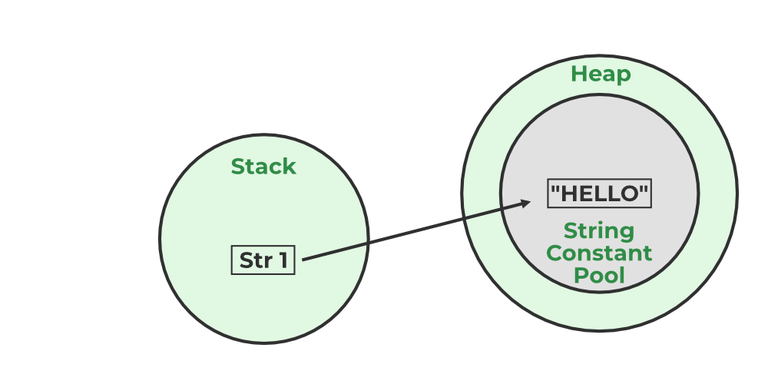
Example:
String str1="Hello";
// "Hello" will be stored in String Pool
// str1 will be stored in stack memory
We can declare the main method without using static and without getting any errors. But, the main method will not be treated as the entry point to the application or the program.
Packages in Java can be defined as the grouping of related types of classes, interfaces, etc providing access to protection and namespace management.
Packages are used in Java in order to prevent naming conflicts, control access, and make searching/locating and usage of classes, interfaces, etc easier.
There are various advantages of defining packages in Java.
There are two types of packages in Java
There are 2 types of data types in Java as mentioned below:
Primitive Data Type: Primitive data are single values with no special capabilities. There are 8 primitive data types:
Non-Primitive Data Type: Reference Data types will contain a memory address of the variable’s values because it is not able to directly store the values in the memory. Types of Non-Primitive are mentioned below:
A byte is an 8-bit signed two-complement integer. The minimum value supported by bytes is -128 and 127 is the maximum value. It is used in conditions where we need to save memory and the limit of numbers needed is between -128 to 127.
No, Java doesn’t provide the support of Pointer. As Java needed to be more secure because which feature of the pointer is not provided in Java.
The default value of the byte datatype in Java is 0.
The default value of the float is 0.0f and of double is 0.0d in Java.
Wrapper, in general, is referred to a larger entity that encapsulates a smaller entity. Here in Java, the wrapper class is an object class that encapsulates the primitive data types.
The primitive data types are the ones from which further data types could be created. For example, integers can further lead to the construction of long, byte, short, etc. On the other hand, the string cannot, hence it is not primitive.
Getting back to the wrapper class, Java contains 8 wrapper classes. They are Boolean, Byte, Short, Integer, Character, Long, Float, and Double. Further, custom wrapper classes can also be created in Java which is similar to the concept of Structure in the C programming language. We create our own wrapper class with the required data types.
The wrapper class is an object class that encapsulates the primitive data types, and we need them for the following reasons:
Declared outside the method, directly invoked by the method.
Declared within the method.
Has a default value.
No default value
It can be used throughout the class.
The scope is limited to the method.
In Java When we haven’t initialized the instance variables then the compiler initializes them with default values. The default values for instances and variables depend on their data types. Some common types of default data types are:
Example:
Output:
byte value0
short value0
int value0
long value0
boolean valuefalse
char value
float value0.0
double value0.0
string valuenull
object valuenull
Array valuenull
In Java, a class variable (also known as a static variable) is a variable that is declared within a class but outside of any method, constructor, or block. Class variables are declared with the static keyword, and they are shared by all instances (objects) of the class as well as by the class itself. No matter how many objects are derived from a class, each class variable would only exist once.
Example:
Number of objects created are 3
There is no default value stored with local variables. Also, primitive variables and objects don’t have any default values.
Instance Variable: A class variable without a static modifier known as an instance variable is typically shared by all instances of the class. These variables can have distinct values among several objects. The contents of an instance variable are completely independent of one object instance from another because they are related to a specific object instance of the class.
Example:
Name John
Class Variable: Class Variable variable can be declared anywhere at the class level using the keyword static. These variables can only have one value when applied to various objects. These variables can be shared by all class members since they are not connected to any specific object of the class.
Example:
Area of circle: 78.53975
The static keyword is used to share the same variable or method of a given class. Static variables are the variables that once declared then a single copy of the variable is created and shared among all objects at the class level.
System.out – It is a PrintStream that is used for writing characters or can be said it can output the data we want to write on the Command Line Interface console/terminal.
Example:
System.err – It is used to display error messages.
Example:
Output:
This is how we throw error with System.err
Although, System.err have many similarities both of them have quite a lot of difference also, let us check them.
It will print to the standard out of the system.
It will print to the standard error.
It is mostly used to display results on the console.
It is mostly used to output error texts.
It gives output on the console with the default(black) color.
It also gives output on the console but most of the IDEs give it a red color to differentiate.
System.in – It is an InputStream used to read input from the terminal Window. We can’t use the System.in directly so we use Scanner class for taking input with the system.in.
Example:
Output:
3
4
Addition: 7

Java brings various Streams with its I/O package that helps the user to perform all the input-output operations. These streams support all types of objects, data types, characters, files, etc to fully execute the I/O operations.
The key difference between them is that byte stream data is read and written by input/output stream classes. Characters are handled by the Reader and Writer classes. In contrast to Reader/Writer classes, which accept character arrays as parameters, input/output stream class methods accept byte arrays. In comparison to input/output streams, the Reader/Writer classes are more efficient, handle all Unicode characters, and are useful for internalization. Use Reader/Writer classes instead of binary data, such as pictures, unless you do so.
Example:
-32 79 -48 32 -22
All the stream classes can be divided into two types of classes that are ByteStream classes and CharacterStream Classes. The ByteStream classes are further divided into InputStream classes and OutputStream classes. CharacterStream classes are also divided into Reader classes and Writer classes. The SuperMost classes for all the InputStream classes is java.io.InputStream and for all the output stream classes is java.io.OutPutStream. Similarly, for all the reader classes, the super-most class is java.io.Reader, and for all the writer classes, it is java.io.Writer.
To read and write data, Java offers I/O Streams. A Stream represents an input source or an output destination, which could be a file, an i/o device, another program, etc. FileInputStream in Java is used to read data from a file as a stream of bytes. It is mostly used for reading binary data such as images, audio files, or serialized objects.
Example:
File file = new File("path_of_the_file");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
In Java, the FileOutputStream function is used to write data byte by byte into a given file or file descriptor. Usually, raw byte data, such as pictures, is written into a file using FileOutputStream.
Example:
File file = new File("path_of_the_file");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
When we are working with the files or stream then to increase the Input/Output performance of the program we need to use the BufferedInputStream and BufferedOutputStream classes. These both classes provide the capability of buffering which means that the data will be stored in a buffer before writing to a file or reading it from a stream. It also reduces the number of times our OS needs to interact with the network or the disk. Buffering allows programs to write a big amount of data instead of writing it in small chunks. This also reduces the overhead of accessing the network or the disk.
BufferedInputStream(InputStream inp);
// used to create the bufferinput stream and save the arguments.
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream output);
// used to create a new buffer with the default size.
Stream filter or Filter Streams returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream that match the given predicate. While working filter() it doesn’t actually perform filtering but instead creates a new stream that, when traversed, contains the elements of initial streams that match the given predicate.
Example:
FileInputStream fis =new FileInoutStream("file_path");
FilterInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
An I/O filter also defined as an Input Output filter is an object that reads from one stream and writes data to input and output sources. It used java.io package to use this filter.
There are two methods to take input from the console in Java mentioned below:
The program demonstrating the use of each method is given below.
Example:
null
Java
Output:
GeeksforGeeks
print, println, and printf all are used for printing the elements but print prints all the elements and the cursor remains in the same line. println shifts the cursor to next line. And with printf we can use format identifiers too.
Operators are the special types of symbols used for performing some operations over variables and values.
All types of operators in Java are mentioned below:
Postfix operators are considered as the highest precedence according to Java operator precedence.
Operators like >> and >>> seem to be the same but act a bit differently. >> operator shifts the sign bits and the >>> operator is used in shifting out the zero-filled bits.
Example:
-8 2147483639
There is only one operator which is right associative which is = operator.
The Dot operator in Java is used to access the instance variables and methods of class objects. It is also used to access classes and sub-packages from the package.
The covariant return type specifies that the return type may vary in the same direction as the subclass. It’s possible to have different return types for an overriding method in the child class, but the child’s return type should be a subtype of the parent’s return type and because of that overriding method becomes variant with respect to the return type.
We use covariant return type because of the following reasons:
The transient keyword is used at the time of serialization if we don’t want to save the value of a particular variable in a file. When JVM comes across a transient keyword, it ignores the original value of the variable and saves the default value of that variable data type.
The sleep() method belongs to the thread class.
Wait() method belongs to the object class.
Sleep does not release the lock that the current thread holds.
wait() release the lock which allows other threads to acquire it.
This method is a static method.
This method is not a static method.
Mainly used to delay a thread for some specific time duration.
Mainly used to pause a thread until notified by another thread.
Sleep() Has Two Overloaded Methods:
Wait() Has Three Overloaded Methods:
StringBuffer
StringBuilder
The string is preferred over StringBuffer as StringBuilder is faster than StringBuffer, but StringBuffer objects are the preferred over as it provides more thread safety.
StringBuffer class in Java is used to represent a changeable string of characters. It offers an alternative to the immutable String class by enabling you to change a string’s contents without constantly creating new objects. Mutable (modifiable) strings are created with the help of the StringBuffer class. The StringBuffer class in Java is identical to the String class except that it is changeable.
Example:
GeeksforGeeks
String using new() is different from the literal as when we declare string it stores the elements inside the stack memory whereas when it is declared using new() it allocates a dynamic memory in the heap memory. The object gets created in the heap memory even if the same content object is present.
Syntax:
String x = new String("ABC");
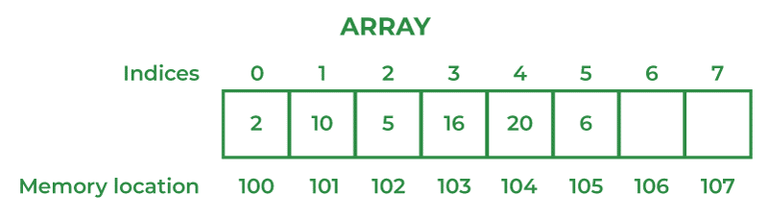
An Array in Java is a data structure that is used to store a fixed-size sequence of elements of the same type. Elements of an array can be accessed by their index, which starts from 0 and goes up to a length of minus 1. Array declaration in Java is done with the help of square brackets and size is also specified during the declaration.
Syntax:
int[] Arr = new int[5];
Arrays in Java are created in heap memory. When an array is created with the help of a new keyword, memory is allocated in the heap to store the elements of the array. In Java, the heap memory is managed by the Java Virtual Machine(JVM) and it is also shared between all threads of the Java Program. The memory which is no longer in use by the program, JVM uses a garbage collector to reclaim the memory. Arrays in Java are created dynamically which means the size of the array is determined during the runtime of the program. The size of the array is specified during the declaration of the array and it cannot be changed once the array is created.
There are two types of arrays i.e., Primitive arrays and References Arrays.
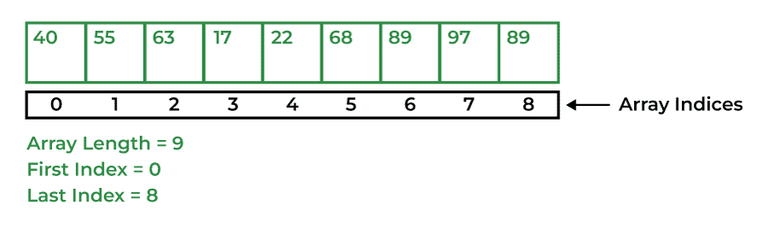
Syntax:
data_type[] Array_Name = new data_type[ArraySize];
The index of an array signifies the distance from the start of the array. So, the first element has 0 distance therefore the starting index is 0.
Syntax:
[Base Address + (index * no_of_bytes)]
Both int array[] and int[] array are used to declare an array of integers in java. The only difference between them is on their syntax no functionality difference is present between them.
int arr[] is a C-Style syntax to declare an Array.
int[] arr is a Java-Style syntax to declare an Array.
However, it is generally recommended to use Java-style syntax to declare an Array. As it is easy to read and understand also it is more consistent with other Java language constructs.
In Java there are multiple ways to copy an Array based on the requirements.
int[] Arr = < 1, 2, 3, 5, 0>;
int[] tempArr = Arr.clone();
int[] Arr = ;
int[] tempArr = new int[Arr.length];
System.arraycopy(Arr, 0, tempArr, 0, Arr.length);
int[] Arr = ;
int[] tempArr = Arrays.copyOf(Arr, Arr.length);
int[] Arr = ;
int[] temArr = Arrays.copyOfRange(Arr, 0, Arr.length);
A jagged Array in Java is just a two-dimensional array in which each row of the array can have a different length. Since all the rows in a 2-d Array have the same length but a jagged array allows more flexibility in the size of each row. This feature is very useful in conditions where the data has varying lengths or when memory usage needs to be optimized.
Syntax:
int[][] Arr = new int[][]
,
,
>;
In Java, it is not possible to make a volatile. Volatile keywords in Java can only be applied to individual variables but not to arrays or collections. The value of the Variable is always read from and written to the main memory when it is defined as volatile rather than being cached in a thread’s local memory. This makes it easier to make sure that all threads that access the variable can see changes made to it.
Paradigm literally means a pattern or a method. Programming paradigms are the methods to solve a program that is of four types namely, Imperative, logical, functional, and object-oriented. When objects are used as base entities upon which the methods are applied, encapsulation or inheritance functionalities are performed, it is known as an object-oriented paradigm.
The main concepts of OOPs in Java are mentioned below:
Object-Oriented Programming Language
Object-Based Programming Language
the new operator is used to create objects, but if we want to decide the type of object to be created at runtime, there is no way we can use the new operator. In this case, we have to use the newInstance() method .
In Java, Classes are the collection of objects sharing similar characteristics and attributes. Classes represent the blueprint or template from which objects are created. Classes are not real-world entities but help us to create objects which are real-world entities.
Static method is associated with a class rather than an object.
The instance method is associated with an object rather than a class.
Static methods can be called using the class name only without creating an instance of a class.
The instance methods can be called on a specific instance of a class using the object reference.
Static methods do not have access to this keyword .
Instance methods have access to this keyword .
Static methods can access only static members of the class.
Instance methods can access both static and non-static methods of the class.
Static methods cannot be overridden because they are resolved at compile time, not at run time. This means that the compiler decides which method to call based on the reference type, not on the object type.
Instance methods can be overridden because they are resolved at run time, not at compile time. This means that the compiler decides which method to call based on the object type, not on the reference type.
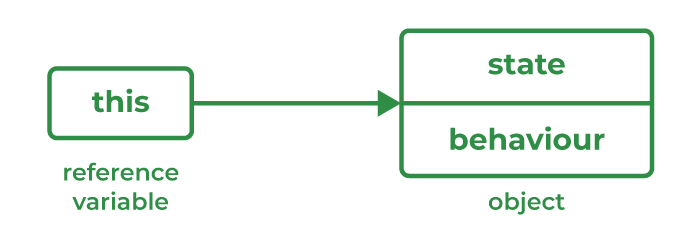
‘this’ is a keyword used to reference a variable that refers to the current object.
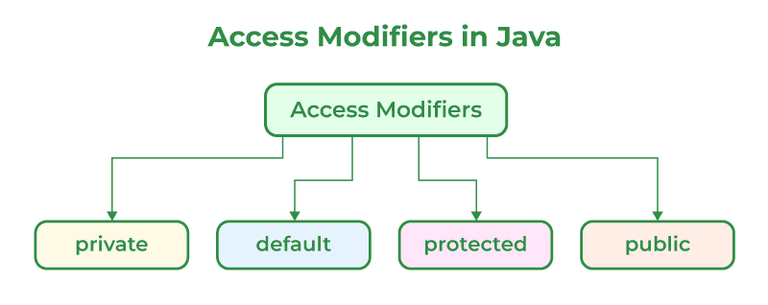
Access Specifiers in Java help to restrict the scope of a class, constructor, variable, method, or data member. There are four types of Access Specifiers in Java mentioned below:
The initial value of an object reference which is defined as an instance variable is a NULL value.
The object is a real-life entity that has certain properties and methods associated with it. The object is also defined as the instance of a class. An object can be declared using a new keyword.
Methods to create objects in Java are mentioned below:
To know more about methods to create objects in Java refer to this article .
There are many advantages and disadvantages of using object cloning as mentioned below:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
There are a few advantages of passing this into a method instead of the current class object itself these are:
Constructor is a special method that is used to initialize objects. Constructor is called when a object is created. The name of constructor is same as of the class.
Example:
// Class Created
class XYZ
private int val;
// Constructor
XYZ()
val=0;
>
>;
If you don’t provide a constructor in a class in Java, the compiler automatically generates a default constructor with no arguments and no operation which is a default constructor.
There are two types of constructors in Java as mentioned below:
Default Constructor: It is the type that does not accept any parameter value. It is used to set initial values for object attributes.
class_Name();
// Default constructor called
Parameterized Constructor: It is the type of constructor that accepts parameters as arguments. These are used to assign values to instance variables during the initialization of objects.
class_Name(parameter1, parameter2. );
// All the values passed as parameter will be
// allocated accordingly
Constructors help to create instances of a class or can be said to create objects of a class. Constructor is called during the initialization of objects. A default constructor is a type of constructor which do not accept any parameter, So whatever value is assigned to properties of the objects are considered default values.
The copy constructor is the type of constructor in which we pass another object as a parameter because which properties of both objects seem the same, that is why it seems as if constructors create a copy of an object.
A private constructor is used if you don’t want any other class to instantiate the object to avoid subclassing. The use private constructor can be seen as implemented in the example.
Example:
Value of a.x = 20 Value of b.x = 20
Java constructors are used for initializing objects. During creation, constructors are called to set attributes for objects apart from this few basic differences between them are:
An interface in Java is a collection of static final variables and abstract methods that define the contract or agreement for a set of linked classes. Any class that implements an interface is required to implement a specific set of methods. It specifies the behavior that a class must exhibit but not the specifics of how it should be implemented.
Syntax:
interface
// constant fields
// methds that are abstract by default
>
Example:
Area of circle is 78.53981633974483 Perimeter of circle is31.41592653589793
An Interface in Java programming language is defined as an abstract type used to specify the behavior of a class. An interface in Java is a blueprint of a behavior. A Java interface contains static constants and abstract methods.
Features of the Interface are mentioned below:
An Interface is recognized as an empty interface (no field or methods) it is called a marker interface. Examples of marker interfaces are Serializable, Cloneable, and Remote interfaces.
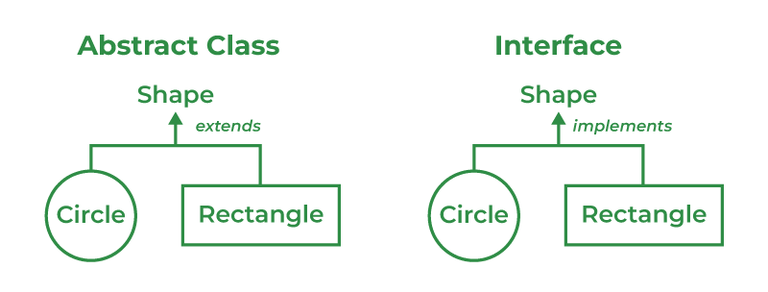
Both abstract and non-abstract methods may be found in an abstract class.
The interface contains only abstract methods.
Abstract Class supports Final methods.
The interface class does not support Final methods.
Multiple inheritance is not supported by the Abstract class.
Multiple inheritances is supported by Interface Class.
Abstract Keyword is used to declare Abstract class.
Interface Keyword is used to declare the interface class.
Abstract Class has members like protected, private, etc.
All class members are public by default.
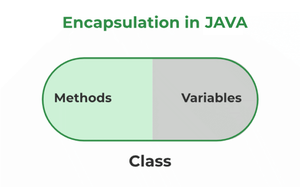
Data Encapsulation is the concept of OOPS properties and characteristics of the classes that The interface is binded together. Basically, it bundles data and methods that operate on that data within a single unit. Encapsulation is achieved by declaring the instance variables of a class as private, which means they can only be accessed within the class.
The advantages of Encapsulation in Java are mentioned below:
The main advantage of Encapsulation in Java is its ability to protect the internal state of an object from external modification or access. It is the is a way of hiding the implementation details of a class from outside access and only exposing a public interface that can be used to interact with the class. The main benefit is of providing a way to control and manage the state and the behavior of an object and also protecting it from modification and unauthorized access at the same time.
Example:
Name is Rohan Age is 29
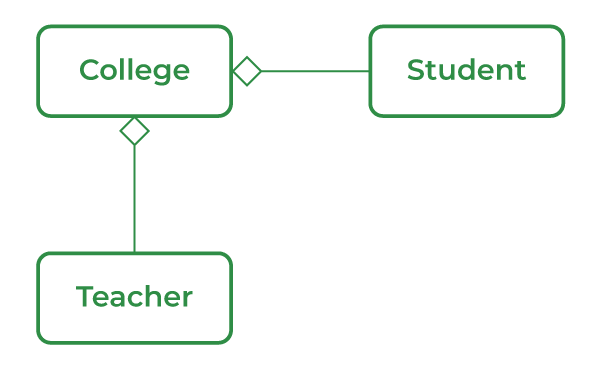
Aggregation is a term related to the relationship between two classes best described as a “has-a” relationship. This kind is the most specialized version of association. It is a unidirectional association means it is a one-way relationship. It contains the reference to another class and is said to have ownership of that class.
‘IS-A’ is a type of relationship in OOPs Java where one class inherits another class.
When an object that belongs to a subclass acquires all the properties and behavior of a parent object that is from the superclass, it is known as inheritance. A class within a class is called the subclass and the latter is referred to as the superclass. Sub class or the child class is said to be specific whereas the superclass or the parent class is generic. Inheritance provides code reusability.
Inheritance is the method by which the Child class can inherit the features of the Super or Parent class. In Java, Inheritance is of four types:
A component of the object-oriented notion known as multiple inheritances allows a class to inherit properties from many parent classes. When methods with the same signature are present in both superclasses and subclasses, an issue arises. The method’s caller cannot specify to the compiler which class method should be called or even which class method should be given precedence.
Note: Java doesn’t support Multiple Inheritance
Example:
Eating Drinking Barking
Inheritance in C++
Inheritance in Java
Yes, there is a limitation of using Inheritance in Java, as because of inheritance one can inherit everything from super class and interface because of which subclass is too clustered and sometimes error-prone when dynamic overriding or dynamic overloading is done in certain situations.
Inheritance is a popular concept of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), in which a class can inherit the properties and methods from any other class, which is referred to as a Parent or superclass. On the other hand in Composition, a class can contain an instance of another class as a member variable which is often referred to as part or a component. Below are some reasons why composition is more advantageous than inheritance:
The association is a relation between two separate classes established through their Objects. It represents Has-A’s relationship.
Composition is a restricted form of Aggregation in which two entities are highly dependent on each other. It represents part-of the relationship.
Composition implies a relationship where the child cannot exist independently of the parent. For example Human heart, the heart doesn’t exist separately from a Human.
It defines a “has a” relationship between the objects
It represents the part-of relationship
Objects are independent of each other.
Objects are dependent on each other.
Represent it by using the empty diamond.
Represent it by using the filled diamond.
Child objects don’t have a lifetime.
Child objects have a lifetime.
No, we can’t inherit a constructor.
Polymorphism is defined as the ability to take more than one form It is of two types namely, Compile time polymorphism or method overloading- a function called during compile time. For instance, take a class ‘area’. Based on the number of parameters it may calculate the area of a square, triangle, or circle. Run time polymorphism or method overriding- links during run time. The method inside a class overrides the method of the parent class.
Dynamic method dispatch is a resolving mechanism for method overriding during the run time. Method overriding is the one where the method in a subclass has the same name, parameters, and return type as a method in the superclass. When the over-ridden method is called through a superclass reference, java determines which version (superclass or subclass) of that method is to be executed based upon the type of an object being referred to at the time the call occurs. Thus the decision is made at run time. This is referred to as dynamic method dispatch.
Method overriding, also known as run time polymorphism is one where the child class contains the same method as the parent class. For instance, we have a method named ‘gfg()’ in the parent class. A method gfg() is again defined in the sub-class. Thus when gfg() is called in the subclass, the method within the class id executed. Here, gfg() within the class overridden the method outside.
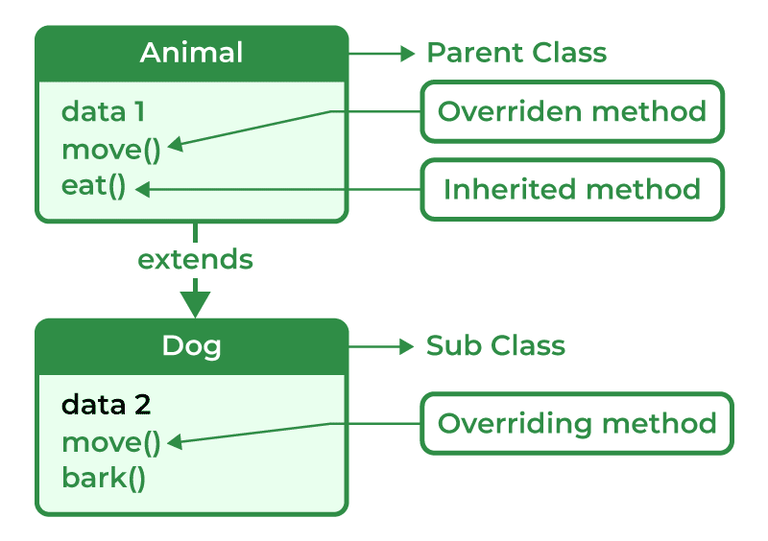
Method overriding is a method to achieve Run-time polymorphism in Java. Method overriding is a feature that allows a child class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by one of its parent classes. When a method in a child class has the same name, the same parameters or signature, and the same return type(or sub-type) as a method in its parent class, then the method in the subclass is said to override the method in the superclass.
In Java, Method Overloading allows different methods to have the same name, but different signatures where the signature can differ by the number of input parameters or type of input parameters, or a mixture of both.
Method overloading in Java is also known as Compile-time Polymorphism, Static Polymorphism, or Early binding . In Method overloading compared to the parent argument, the child argument will get the highest priority.
No, as static methods are part of the class rather than the object so we can’t override them.
Yes, since the overloaded method is a completely different method in the eyes of the compiler. Overriding isn’t the same thing at all. The decision as to which method to call is deferred to runtime.
Yes in Java we can overload the main method to call the main method with the help of its predefined calling method.
Method Overloading: It is also known as Compile Time Polymorphism. In method overloading two or more methods are shared in the same class with a different signature.
Example:
multiply() with 2 parameters 20 multiply() with 3 parameters 24 multiply() with 4 parameters 24
Method Overriding: Method Overriding occurs when a subclass can provide the implementation of a method which is already defined in the parent class or superclass. The return type, name and arguments must be similar to the methods in superclass.
Example:
drive() method of derived class Car is driving. drive() method of base class driving the Car. drive() method of derived class Car is driving.
When two or multiple methods are in the same class with different parameters but the same name.
When a subclass provides its own implementation of a method that is already defined in the parent class.
Method overloading can only happen in the same class or between a subclass or parent class.
Method overriding can only happen in Subclass.
When an error occurs it is caught at the compile time of the program.
When an error occurs it is caught at Runtime of the program.
Example of Compile Time Polymorphism.
Example of Run Time Polymorphism.
Method Overloading may or may not require Inheritance.
Method overriding always needs Inheritance.
It occurs within the class.
It is performed in two classes with an inheritance relationship.
It is not possible to override the private methods in Java. Method overriding is where the method in the subclass is implemented instead of the method from the parent class. The private methods are accessible only within the class in which it is declared. Since this method is not visible to other classes and cannot be accessed, it cannot be overridden.
In Java, it is not possible to modify the overridden method’s scope. The subclass method’s scope must be equal to or wider than the Superclass method’s overridden method’s scope. The overridden method in the subclass, for instance, can have a public scope or a more accessible scope like protected or default if the overridden method in the superclass has a public scope. It cannot, however, have a more exclusive scope like private.
We can modify the throws clause of the Superclass method with some limitations, we can change the throws clause of the superclass method while overriding it in the subclass. The subclass overridden method can only specify unchecked exceptions if the superclass method does not declare any exceptions. If the superclass method declares an exception, the subclass method can declare the same exception, a subclass exception, or no exception at all. However, the subclass method cannot declare a parent exception that is broader than the ones declared in the superclass method.
Yes, Java supports virtual functions. Functions are by default virtual and can be made non-virtual using the final keyword.
Abstraction refers to the act of representing essential features without including background details. The detailed information or the implementation is hidden. The most common example of abstraction is a car, we know how to turn on the engine, accelerate and move, however, the way engine works, and its internal components are complex logic hidden from the general users. This is usually done to handle the complexity.
A class declared as abstract, cannot be instantiated i.e., the object cannot be created. It may or may not contain abstract methods but if a class has at least one abstract method, it must be declared abstract.
Example of an abstract class with abstract method:
Abstract class example
An abstract method is used when we want to use a method but want to child classes to decide the implementation in that case we use Abstract methods with the parent classes.
Serialization in the child class if the base class is implementing the Serializable interface then we can avoid it by defining the writeObject() method and throwing NotSerializableException().
Collections are units of objects in Java. The collection framework is a set of interfaces and classes in Java that are used to represent and manipulate collections of objects in a variety of ways. The collection framework contains classes(ArrayList, Vector, LinkedList, PriorityQueue, TreeSet) and multiple interfaces (Set, List, Queue, Deque) where every interface is used to store a specific type of data.
Collection framework implements
Collection interface: Collection is the primary interface available that can be imported using java.util.Collection.
Syntax:
public interface Collection extends iterable
An ArrayList can be synchronized using two methods mentioned below:
public static List synchronizedList(List list)
ArrayList is in need even when we have Vectors because of certain reasons:
Generic arrays can’t be created because an array carries type information of its elements at runtime because of which during runtime it throw ‘ArrayStoreException’ if the elements’ type is not similar. Since generics type information gets erased at compile time by Type Erasure, the array store check would have been passed where it should have failed.
The elements of a regular array in Java are stored in contiguous memory locations, meaning that each element is stored in a sequential block of memory. This allows easy access to any element by its index because the address can be calculated using the base address of the array and the size of each element
In contrast, the ArrayList class implements a dynamic array, which means that its size can change as elements are added or removed. ArrayList elements are also stored in contiguous memory locations, similar to arrays. However, when an ArrayList reaches its capacity and more elements need to be added, a new, larger underlying array is created. The elements from the old array are then copied to the new one. This process ensures that the ArrayList can grow dynamically while keeping the elements in contiguous memory locations.
There are multiple methods to convert List into ArrayList
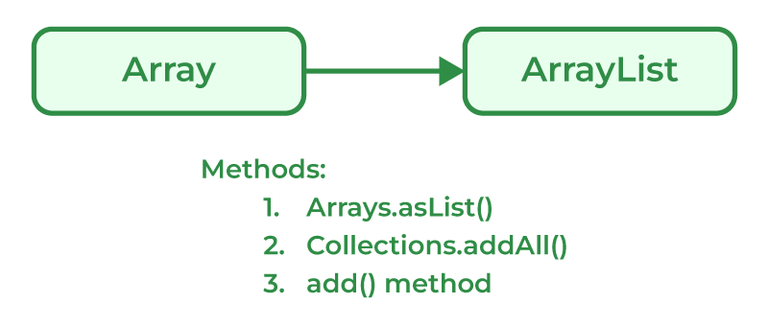
Programmers can convert an Array to ArrayList using asList() method of the Arrays class. It is a static method of the Arrays class that accepts the List object.
Syntax:
Arrays.asList(item)
Example:
[Abc, Def, Ghi, Jkl]
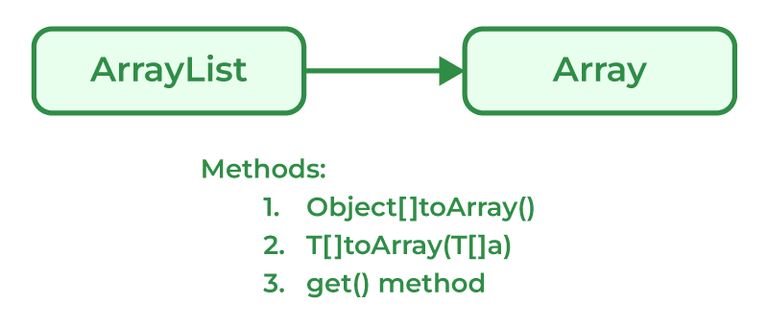
Java programmers can convert ArrayList to
Syntax:
List_object.toArray(new String[List_object.size()])
Example:
1 2 3 2 1
Due to ArrayLists array-based nature, it grows dynamically in size ensuring that there is always enough room for elements. When an ArrayList element is first created, the default capacity is around 10-16 elements which basically depends on the Java version. ArrayList elements are copied over from the original array to the new array when the capacity of the original array is full. As the ArrayList size increases dynamically, the class creates a new array of bigger sizes and it copies all the elements from the old array to the new array. Now, the reference of the new array is used internally. This process of dynamically growing an array is known as resizing.
Vectors in Java are similar and can store multiple elements inside them. Vectors follow certain rules mentioned below:
Syntax:
Vector gfg = new Vector(size, increment);
An ArrayList can be made ready only using the method provided by Collections using the Collections.unmodifiableList() method.
Syntax:
array_readonly = Collections.unmodifiableList(ArrayList);
Example:
Initial list: [X, Y, Z] ReadOnly ArrayList: [X, Y, Z] Attempting to add element to the ReadOnly ArrayList Exception is thrown : java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
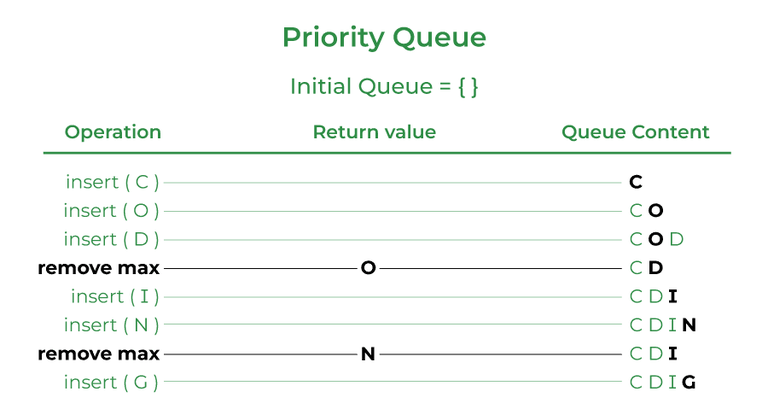
A priority queue is an abstract data type similar to a regular queue or stack data structure. Elements stored in elements are depending upon the priority defined from low to high. The PriorityQueue is based on the priority heap.
Syntax:
LinkedList class is Java that uses a doubly linked list to store elements. It inherits the AbstractList class and implements List and Deque interfaces. Properties of the LinkedList Class are mentioned below:
LinkedList list_name=new LinkedList();
A Stack class in Java is a LIFO data structure that implements the Last In First Out data structure. It is derived from a Vector class but has functions specific to stacks. The Stack class in java provides the following methods:
Sets are collections that don’t store duplicate elements. They don’t keep any order of the elements. The Java Collections framework provides several implementations of the Set interface, including:
The HashSet class implements the Set interface in the Java Collections Framework and is a member of the HashSet class. Unlike duplicate values, it stores a collection of distinct elements. In this implementation, each element is mapped to an index in an array using a hash function, and the index is used to quickly access the element. It produces an index for the element in the array where it is stored based on the input element. Assuming the hash function distributes the elements among the buckets appropriately, the HashSet class provides constant-time performance for basic operations (add, remove, contain, and size).
The LinkedHashSet is an ordered version of Hashset maintained by a doubly-linked List across all the elements. It is very helpful when iteration order is needed. During Iteration in LinkedHashSet, elements are returned in the same order they are inserted.
Syntax:
LinkedHashSet hs = new LinkedHashSet();
Example:
Values:[1, 2, 5, 3]
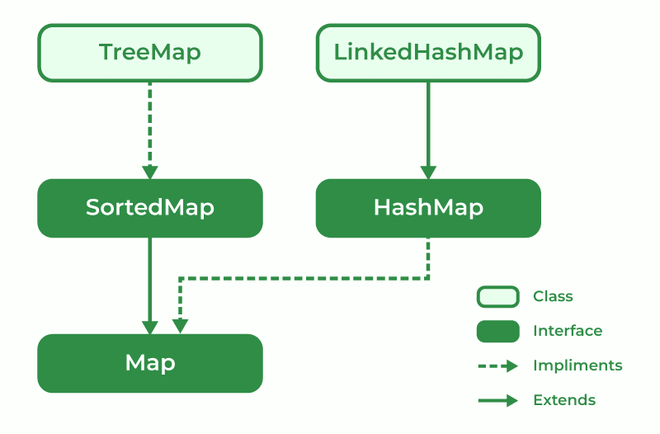
The map interface is present in the Java collection and can be used with Java.util package. A map interface is used for mapping values in the form of a key-value form. The map contains all unique keys. Also, it provides methods associated with it like containsKey(), contains value (), etc.
There are multiple types of maps in the map interface as mentioned below:
TreeMap is a type of map that stores data in the form of key-value pair. It is implemented using the red-black tree. Features of TreeMap are :
EnumSet is a specialized implementation of the Set interface for use with enumeration type. A few features of EnumSet are:
Syntax:
public abstract class EnumSet>
Parameter: E specifies the elements.
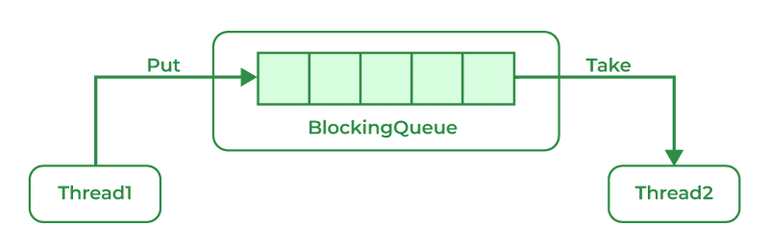
A blocking queue is a Queue that supports the operations that wait for the queue to become non-empty while retrieving and removing the element, and wait for space to become available in the queue while adding the element.
Syntax:
public interface BlockingQueue extends Queue
Parameters: E is the type of elements stored in the Collection
ConcurrentHashMap is implemented using Hashtable.
Syntax:
public class ConcurrentHashMap
extends AbstractMap
implements ConcurrentMap, Serializable
Parameters : K is the key Object type and V is the value Object type
Yes, we can use any class as a Map Key if it follows certain predefined rules mentioned below:
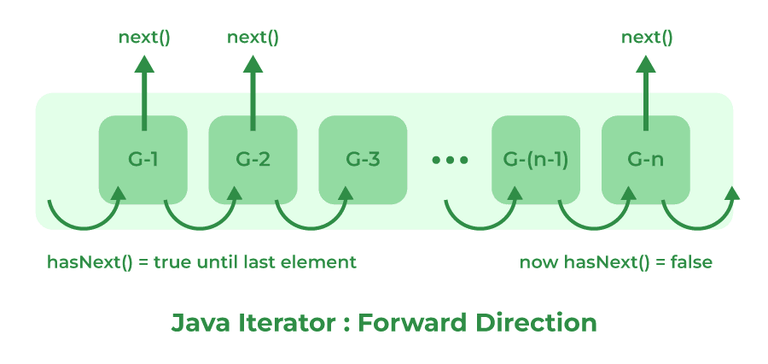
The Iterator interface provides methods to iterate over any Collection in Java. Iterator is the replacement of Enumeration in the Java Collections Framework. It can get an iterator instance from a Collection using the _iterator()_ method. It also allows the caller to remove elements from the underlying collection during the iteration.
Enumeration is a user-defined data type. It is mainly used to assign names to integral constants, the names make a program easy to read and maintain. The main objective of the enum is to define user-defined data types.
Example:
// A simple enum example where enum is declared
// outside any class (Note enum keyword instead of
// class keyword)
enum Color
RED, GREEN, BLUE;
>
The Collection is an Interface.
Collections is a class.
It provides the standard functionality of data structure.
It is to sort and synchronize the collection elements.
It provides the methods that can be used for the data structure.
It provides static methods that can be used for various operations.
Array
ArrayList
Single-dimensional or multidimensional
For and for each used for iteration
Here iterator is used to traverse riverArrayList
length keyword returns the size of the array.
size() method is used to compute the size of ArrayList.
The array has Fixed-size.
ArrayList size is dynamic and can be increased or decreased in size when required.
It is faster as above we see it of fixed size
It is relatively slower because of its dynamic nature
Primitive data types can be stored directly in unlikely objects.
Primitive data types are not directly added to unlikely arrays, they are added indirectly with help of autoboxing and unboxing
They can not be added here hence the type is in the unsafe.
They can be added here hence makingArrayList type-safe.
The assignment operator only serves the purpose
Here a special method is used known as add() method
Array in Java has a fixed size.
Collections in Java have dynamic sizes.
In an Array, Elements are stored in contiguous memory locations.
In Collections, Elements are not necessarily stored in contiguous memory locations.
Objects and primitive data types can be stored in an array.
We can only store objects in collections.
Manual manipulation is required for resizing the array.
Resizing in collections is handled automatically.
The array has basic methods for manipulation.
Collections have advanced methods for manipulation and iteration.
The array is available since the beginning of Java.
Collections were introduced in Java 1.2.
ArrayList is Implemented as an expandable Array.
LinkedList is Implemented as a doubly-linked list.
In ArrayList, Elements are stored in contiguous memory locations
LinkedList Elements are stored in non-contiguous memory locations as each element has a reference to the next and previous elements.
ArrayLists are faster for random access.
LinkedLists are faster for insertion and deletion operations
ArrayLists are more memory efficient.
LinkedList is less memory efficient
ArrayLists Use more memory due to maintaining the array size.
LinkedList Uses less memory as it only has references to elements
The search operation is faster in ArrayList.
The search operation is slower in LinkedList
ArrayList is i mplemented as a resizable array.
Vector is i mplemented as a synchronized, resizable array.
ArrayList is not synchronized.
The vector is synchronized.
ArrayLists are Faster for non-concurrent operations.
Vector is Slower for non-concurrent operations due to added overhead of synchronization.
ArrayLists were Introduced in Java 1.2.
Vector was Introduced in JDK 1.0.
Recommended for use in a single-threaded environment.
Vectors are Recommended for use in a multi-threaded environment.
The default initial capacity of ArrayLists is 10.
In Vectors, the default initial capacity is 10 but the default increment is twice the size.
ArrayList performance is high.
Vector performance is low.
Can traverse elements present in Collection only in the forward direction.
Can traverse elements present in Collection both in forward and backward directions.
Used to traverse Map, List, and Set.
Can only traverse List and not the other two.
Indexes can’t be obtained using Iterator
It has methods like nextIndex() and previousIndex() to obtain indexes of elements at any time while traversing the List.
Can’t modify or replace elements present in Collection
Can modify or replace elements with the help of set(E e)
Can’t add elements, and also throws ConcurrentModificationException.
Can easily add elements to a collection at any time.
Certain methods of Iterator are next(), remove(), and hasNext().
Certain methods of ListIterator are next(), previous(), hasNext(), hasPrevious(), add(E e).
HashMap is not synchronized
HashTable is synchronized
One key can be a NULL value
NULL values not allowed
The iterator is used to traverse HashMap.
Both Iterator and Enumertar can be used
HashMap is faster.
HashTable is slower as compared to HashMap.
The Iterator can traverse both legacies as well as non-legacy elements.
Enumeration can traverse only legacy elements.
The Iterator is fail-fast.
Enumeration is not fail-fast.
The Iterators are slower.
Enumeration is faster.
The Iterator can perform a remove operation while traversing the collection.
The Enumeration can perform only traverse operations on the collection.
The interface is present in java.lang package.
The Interface is present in java.util package.
Provides compareTo() method to sort elements.
Provides compare() method to sort elements.
It provides single sorting sequences.
It provides multiple sorting sequences.
The logic of sorting must be in the same class whose object you are going to sort.
The logic of sorting should be in a separate class to write different sorting based on different attributes of objects.
Method sorts the data according to fixed sorting order.
Method sorts the data according to the customized sorting order.
It affects the original class.
It doesn’t affect the original class.
Implemented frequently in the API by Calendar, Wrapper classes, Date, and String.
It is implemented to sort instances of third-party classes.
The Set interface is implemented using java.util package.
The map is implemented using java.util package.
It can extend the collection interface.
It does not extend the collection interface.
It does not allow duplicate values.
It allows duplicate values.
The set can sort only one null value.
The map can sort multiple null values.
A FailFast iterator is an iterator that throws a ConcurrentModificationException if it detects that the underlying collection has been modified while the iterator is being used. This is the default behavior of iterators in the Java Collections Framework. For example, the iterator for a HashMap is FailFast.
Example:
Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
A FailSafe iterator does not throw a ConcurrentModificationException if the underlying collection is modified while the iterator is being used. Alternatively, it creates a snapshot of the collection at the time the iterator is created and iterates over the snapshot. For example, the iterator for a ConcurrentHashMap is FailSafe.
Example:
An Exception is an Event that interrupts the normal flow of the program and requires special processing. During the execution of a program, errors and unplanned occurrences can be dealt with by using the Java Exception Handling mechanism. Below are some reasons why Exceptions occur in Java:
There are generally two types of exceptions in Java:
Errors
Exceptions
Recovering from Errors is not possible.
Recover from exceptions by either using a try-catch block or throwing exceptions back to the caller.
Errors are all unchecked types in Java.
It includes both checked as well as unchecked types that occur.
Errors are mostly caused by the environment in which the program is running.
The program is mostly responsible for causing exceptions.
Errors can occur at compile time as well as run time. Compile Time: Syntax Error, Run Time: Logical Error.
All exceptions occur at runtime but checked exceptions are known to the compiler while unchecked are not.
They are defined in java.lang.Error package.
They are defined in java.lang.Exception package
Examples : java.lang.StackOverflowError, java.lang.OutOfMemoryError
Examples : Checked Exceptions: SQLException, IOException Unchecked Exceptions: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException, NullPointerException, ArithmeticException.
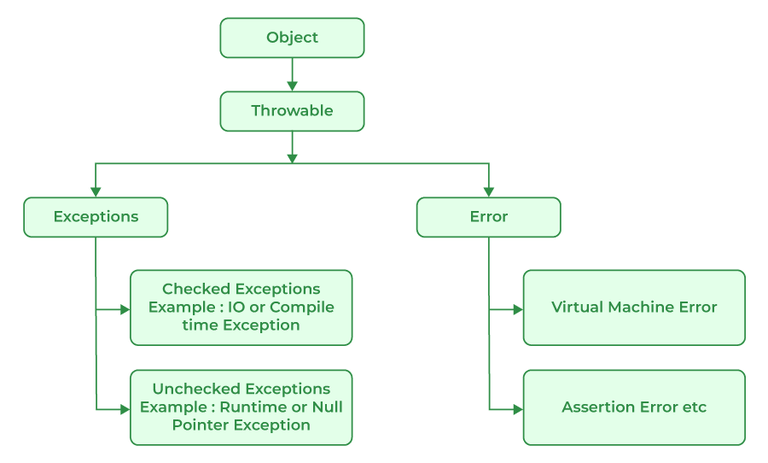
All exception and error types in Java are subclasses of the class throwable, which is the base class of the hierarchy. This class is then used for exceptional conditions that user programs should catch. NullPointerException is an example of such an exception. Another branch, error is used by the Java run-time system to indicate errors having to do with the JRE. StackOverflowError is an example of one of such error.
Runtime Exceptions are exceptions that occur during the execution of a code, as opposed to compile-time exceptions that occur during compilation. Runtime exceptions are unchecked exceptions, as they aren’t accounted for by the JVM.
Examples of runtime exceptions in Java include:
Unlike checked exceptions, runtime exceptions do not require a declaration in the throws clause or capture in a try-catch block. However, handling runtime exceptions is advisable in order to provide meaningful error messages and prevent a system crash. Because runtime exceptions provide more specific information about the problem than checked exceptions, they enable developers to detect and correct programming errors more easily and quickly.
It is a type of run-time exception that is thrown when the program attempts to use an object reference that has a null value. The main use of NullPointerException is to indicate that no value is assigned to a reference variable, also it is used for implementing data structures like linked lists and trees.
ArrayStoreException is thrown when an attempt is made to store the wrong type of object in an array of objects.
Example:
Example:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayStoreException: java.lang.Integer
at GFG.main(GFG.java:6)
Checked Exceptions are the exceptions that are checked during compile time of a program. In a program, if some code within a method throws a checked exception, then the method must either handle the exception or must specify the exception using the throws keyword.
Checked exceptions are of two types:
Unchecked are the exceptions that are not checked at compile time of a program. Exceptions under Error and RuntimeException classes are unchecked exceptions, everything else under throwable is checked.

Error is an illegal operation performed by the user which causes abnormality in the program. Exceptions are the unexpected events or conditions that comes while running the program, exception disrupts the normal flow of the program’s instructions.
Errors and Exceptions both have a common parent class which is java.lang.Throwable class.
No, It is not necessary to use catch block after try block in Java as we can create another combination with finally block. Finally is the block which runs despite the fact that the exception is thrown or not.
Exception propagation is a process in which the exception is dropped from to the top to the bottom of the stack. If not caught once, the exception again drops down to the previous method, and so on until it gets caught or until it reaches the very bottom of the call stack.
System.exit(int) has the capability to throw SecurityException. So, if in case of security, the exception is thrown then finally block will be executed otherwise JVM will be closed while calling System. exit(0) because of which finally block will not be executed.
It is the process of creating an exact copy of any object. In order to support this, a java class has to implement the Cloneable interface of java.lang package and override the clone() method provided by the Object class the syntax of which is:
Protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException< return (Object)super.clone();>In case the Cloneable interface is not implemented and just the method is overridden, it results in CloneNotSupportedException in Java.
Exceptions are responsible for abruptly terminating the running of the program while executing and the code written after the exception occurs is not executed.
The final keyword is used to make functions non-virtual. By default, all the functions are virtual so to make it non-virtual we use the final keyword.
final is a keyword is used with the variable, method, or class so that they can’t be overridden.
Example:
Output:
./GFG.java:6: error: cannot assign a value to final variable x
x=50;
^
1 error
finally is a block of code used with “try-catch” in exception handling. Code written in finally block runs despite the fact exception is thrown or not.
Example:
Try block Always runs even without exceptions
It is a method that is called just before deleting/destructing the objects which are eligible for Garbage collection to perform clean-up activity.
Main function running
It represents the current instance of the class.
It represents the current instance of the parent class.
Calls the default constructor of the same class.
Calls the default constructor of the base class.
Access the methods of the same class.
Access the methods of the parent class.
Points current class instance.
Points the superclass instance.
Multitasking in Java refers to a program’s capacity to carry out several tasks at once. Threads, which are quick operations contained within a single program, can do this. Executing numerous things at once is known as multitasking.
Example:
Multithreaded programs in Java contain threads that run concurrently instead of running sequentially. A computer can use its resources more efficiently by combining multiple tasks at once. Any program with multithreading allows more than one user to simultaneously use the program without running multiple copies. A multithreaded program is designed to run multiple processes at the same time which can improve the performance of a program and allows the program to utilize multiple processors and improves the overall throughput.
There are multiple advantages of using multithreading which are as follows:
Multithreading is a Java feature that allows concurrent execution of two or more parts of a program for maximum utilization of the CPU. In general, threads are small, lightweight processes with separate paths of execution. These threads use shared memory, but they act independently, thus if any one thread fails it does not affect the other threads. There are two ways to create a thread:
We create a class that extends the java.lang.Thread class . This class overrides the run() method available in the Thread class. A thread begins its life inside run() method.
Syntax:
public class MyThread extends Thread
public void run()
// thread code goes here
>
>
We create a new class that implements java.lang.Runnable interface and override run() method. Then we instantiate a Thread object and call the start() method on this object.
Syntax:
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable
public void run()
// thread code goes here
>
>
Threads in Java are subprocess with lightweight with the smallest unit of processes and also has separate paths of execution. These threads use shared memory but they act independently hence if there is an exception in threads that do not affect the working of other threads despite them sharing the same memory. A thread has its own program counter, execution stack, and local variables, but it shares the same memory space with other threads in the same process. Java provides built-in support for multithreading through the Runnable interface and the Thread class .
A process and a thread are both units of execution in a computer system, but they are different in several ways:
A process is a program in execution.
A thread is a single sequence of instructions within a process.
The process takes more time to terminate.
The thread takes less time to terminate.
The process takes more time for context switching.
The thread takes less time for context switching.
The process is less efficient in terms of communication.
Thread is more efficient in terms of communication.
The process is isolated.
Threads share memory.
The process has its own Process Control Block, Stack, and Address Space.
Thread has Parents’ PCB, its own Thread Control Block, and Stack and common Address space.
The process does not share data with each other.
Threads share data with each other.
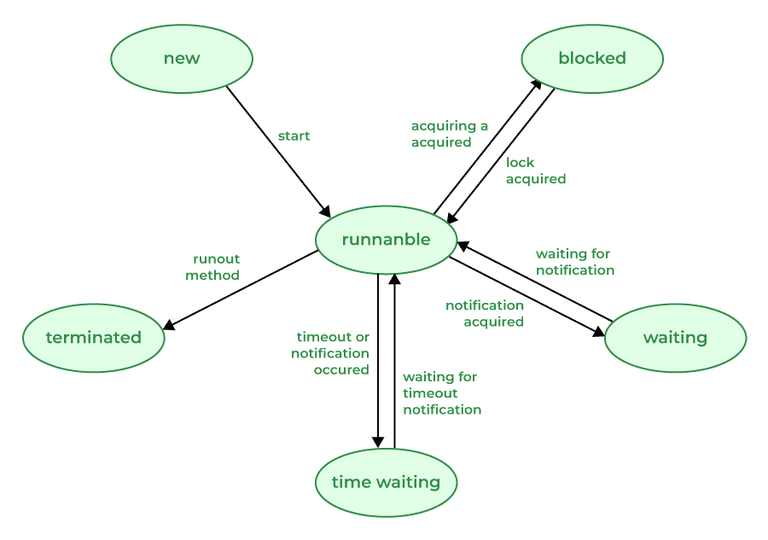
A thread in Java at any point in time exists in any one of the following states. A thread lies only in one of the shown states at any instant:
The suspend() method of the Thread class in Java temporarily suspends the execution of a thread. When a thread is suspended it goes into a blocked state and it would not be scheduled by the operating system which means that it will not be able to execute its task until it is resumed. There are more safer and flexible alternatives to the suspend() methods in the modern java programming language. This method does not return any value.
Syntax:
public final void suspend();
Example:
Output:
Thread running: 0
Thread running: 1
Thread running: 2
Suspended thread
Resumed thread
Thread running: 3
Thread running: 4
Thread running: 5
Thread running: 6
Thread running: 7
Thread running: 8
Thread running: 9
Java provides built-in support for multithreaded programming. The main thread is considered the parent thread of all the other threads that are created during the program execution. The main thread is automatically created when the program starts running. This thread executes the main method of the program. It is responsible for executing the main logic of the Java program as well as handling the user input operations. The main thread serves as the base thread from which all other child threads are spawned.
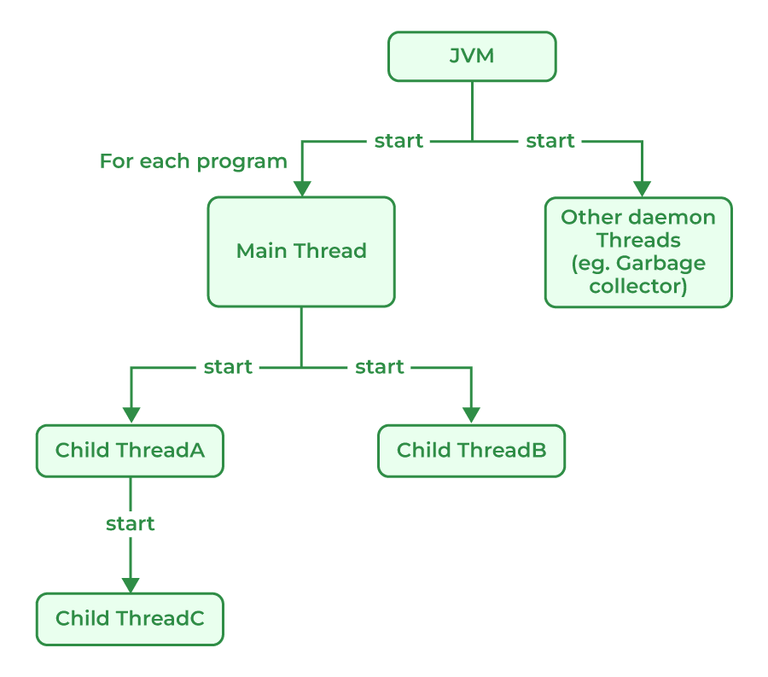
A daemon thread in Java is a low-priority thread that is used to perform background operations or tasks which are used to perform continuously. such as Garbage collection, Signal dispatches, Action listeners, etc. Daemon threads in Java have lower priority than user threads, which means they can only execute when no user threads are running. Daemon threads in Java are useful features that are required for background tasks that do not require explicit shutdown or finalization. It allows more efficient use of system resource and are used to simplify resources and can simplify long-running tasks.
Thread is a lightweight process that runs concurrently with the other thread inside a single process. Each thread can execute a different task and share the resources within a single process. Thread in Java can enter the waiting state in many different ways:
Java uses a technique called time-sharing, commonly referred to as time-slicing, to implement multi-threading on computers with a single CPU. The appearance of parallel execution is created by the CPU switching between active threads. The operating system is in charge of allocating CPU time to each thread sequentially and scheduling the threads.
In order to stop threads from interacting with one another and creating race situations or other issues, Java has a number of ways to govern the behavior of threads, including synchronization and locking. It is feasible to create multi-threaded programmers that operate correctly and effectively on a machine with a single CPU by regulating the interaction between threads and making sure that crucial code parts are synchronized. In contrast to running the same program on a computer with multiple CPUs or cores, multi-threading on a single CPU can only give the appearance of parallelism, and actual performance gains may be modest. The operating system divides the CPU time that is available when numerous threads are running on a single CPU into small time slices and gives each thread a time slice to execute. Rapid switching between the threads by the operating system creates the appearance of parallel execution. The switching between threads appears to be immediate because the time slices are often very tiny, on the order of milliseconds or microseconds.
Priorities in threads is a concept where every thread is having a priority which in layman’s language one can say every object is having priority here which is represented by numbers ranging from 1 to 10. There are different types of thread properties in Java mentioned below:
By default, the thread is assigned NORM_PRIORITY.
For Java, Garbage collection is necessary to avoid memory leaks which can cause the program to crash and become unstable. There is no way to avoid garbage collection in Java. Unlike C++, Garbage collection in Java helps programmers to focus on the development of the application instead of managing memory resources and worrying about memory leakage. Java Virtual Machine (JVM) automatically manages the memory periodically by running a garbage collector which frees up the unused memory in the application. Garbage collection makes Java memory efficient because it removes unreferenced objects from the heap memory.
Apart from many advantages, Garbage Collector has certain drawbacks mentioned below:
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) removes objects that are no longer in use using a garbage collector which periodically checks and removes these objects. There are different types of garbage collection in the JVM, each with different characteristics and performance implications. The main types of garbage collection are:
Major garbage collection works on the survivor space and Minor garbage collection works on the Eden space to perform a mark-and-sweep routine. And we can identify both of them based on the output where the minor collection prints “GC”, whereas the major collection prints “Full GC” for the case where the garbage collection logging is enabled with “-XX:PrintGCDetails” or “verbose:gc”.
In Java Memory leaks can be caused by a variety of factors, such as not closing resources properly, holding onto object references longer than necessary, or creating too many objects unnecessarily. There are situations in which garbage collector does not collect objects because there is a reference to those objects. In these situations where the application creates lots of objects and does not use them and every object has some valid references, a Garbage collector in Java cannot destroy the objects. These useless objects which do not provide any value to the program are known as Memory leaks. Memory leaks can impact garbage collection negatively by preventing the garbage collector from reclaiming unused memory. This behavior will lead to slow performance or sometimes system failure. In a program, it is important to avoid memory leaks by managing resources and object references properly.
Example:
Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
at java.base/java.util.Vector.(Vector.java:142)
at java.base/java.util.Vector.(Vector.java:155)
at GFG.main(GFG.java:9)
Regular Expressions or Regex in Java is an API used for searching and manipulating of strings in Java. It creates String patterns that can extract the data needed from the strings or can generalize a pattern.
There are 3 Classes present in java.util.regex mentioned below:
Also, apart from the 3 classes package consists of a single interface MatchResult Interface which can be used for representing the result of a match operation.
regex = “^(?=.*[0-9])(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[@#$%^&-+=()])(?=\\S+$).$”
Explanation:
JDBC standard API is used to link Java applications and relational databases. It provides a collection of classes and interfaces that let programmers to use the Java programming language to communicate with the database. The classes and interface of JDBC allow the application to send requests which are made by users to the specified database. There are generally four components of JDBC by which it interacts with the database:
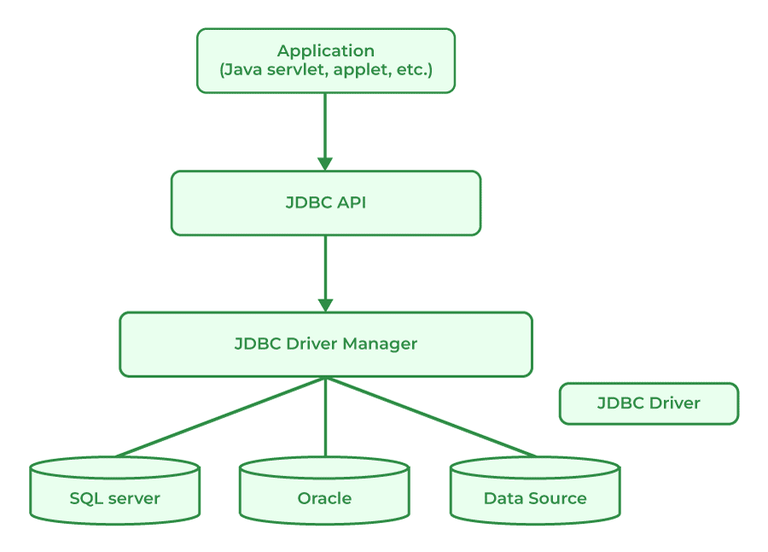
JDBC Driver is a software component that is used to enable a Java application to interact with the database. JDBC provides the implementation of the JDBC API for a specific database management system, which allows it to connect the database, execute SQL statements and retrieve data. There are four types of JDBC drivers:
There are certain steps to connect the database and Java Program as mentioned below:
JDBC API components provide various methods and interfaces for easy communication with the databases also it provides packages like java Se and java EE which provides the capability of write once run anywhere (WORA).
Syntax:
java.sql.*;
Java database connectivity interface (JDBC) is a software component that allows Java applications to interact with databases. To enhance the connection, JDBC requires drivers for each database.
JDBC ResultSet interface is used to store the data from the database and use it in our Java Program. We can also use ResultSet to update the data using updateXXX() methods. ResultSet object points the cursor before the first row of the result data. Using the next() method, we can iterate through the ResultSet.
A JDBC RowSet provides a way to store the data in tabular form. RowSet is an interface in java that can be used within the java.sql package. The connection between the RowSet object and the data source is maintained throughout its life cycle. RowSets are classified into five categories based on implementation mentioned below:
JDBC DriverManager class acts as an interface for users and Drivers. It is used in many ways as mentioned below:
Iterable provides a way to iterate over a sequence of elements.
Iterator helps in iterating over a collection of elements sequentially.
Examples are List, Queue, and Set.
Examples are ListIterator, Enumeration, and ArrayIterator.
List allows duplicates.
Set does not allow duplicate values.
List is accessed by index.
Set is accessed by hashcode.
Multiple null elements can be stored.
Null element can store only once.
Examples are ArrayList, LinkedList, etc.
Examples are HashSet and TreeSet. LinkedHashSet etc.
List interface allows duplicate elements.
Map does not allow duplicate elements.
List maintains insertion order.
Map do not maintain insertion order.
Multiple null elements can be stored.
The map allows a single null key at most and any number of null values.
The list provides get() method to get the element at a specified index.
The map does not provide a get method to get the elements at a specified index.
List is Implemented by ArrayList, etc.
Map is Implemented by HashMap, TreeMap, LinkedHashMap
Queue data structure is used to store elements, and is used to perform operations like enqueue, dequeue from back or end of the queue.
Stack data structure is used to store elements, and is used to perform operations like push, pop from top of the stack.
Queue data structure Implements FIFO order.
Stack data structure Implements LIFO order.
Insertion and deletion in queues take place from the opposite ends of the list. Deletion takes place from the front of the list and insertion takes place at the rear of the list.
Insertion and deletion in stacks take place only from one end of the list called the top.
Insert operation is called enqueue operation.
Insert operation is called Push operation.
Queue is generally used to solve problems related to sequential processing.
Stack is generally used to solve problems related to recursion.
It uses Queue as an underlying data structure.
It uses a Set as an underlying data structure.
This data structure allows duplicate elements
This data structure does not allow duplicate elements
Priority Queue is Implemented by PriorityQueue class.
TreeSet is implemented by TreeSet class.
PriorityQueue comes in JDK 1.5.
TreeSet comes in JDK 1.4.
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
reeSet ts = new TreeSet<>();
Singly Linked List
Doubly Linked List
Singly Linked List contain only two segments i.e, Data and Link.
Doubly Linked List contains three segments i.e, Data, and two pointers.
Traversal in a singly linked list is possible in only a forward direction.
Traversal in a doubly linked list is only possible in both directions forward as well as backward.
It uses less memory as every single node has only one pointer.
It requires more memory than a singly linked list as each node has two pointers.
Easy to use and insert nodes at the beginning of the list.
Slightly more complex to use and easy to insert at the end of the list.
The time complexity of insertion and deletion is O(n).
The time complexity of insertion and deletion is O(1).


Failsfast fails immediately when it detects concurrent modification during the time of iteration.
Failsafe continues to iterate over the original collection and also creates a copy to modify.
Failfast is generally used in single-threaded environments.
Failsafe is used in multithreaded environments.
Failfast does not allow any modification while iteration.
Failsafe allows modification during the time of iteration.
Failfast is fast compared to failsafe as it does not involve the copying of the collection.
Failsafe is generally slow compared to failfast.
FailFast throws ConcurrentModificationException if the collection is modified during iteration.
FailSafe does not throws any exception but instead, it creates a copy of the collection to iterate.
Hasmap uses a hashtable in order to store key-value pairs.
Treemap uses Red-black trees to store key-value pair.
Hashmap does not maintain any specific order for key-value pairs.
Treemap maintains a natural ordering based on the keys.
Order of iteration is not guaranteed in the hashmap.
Iteration is of sorted order based on keys.
Hashmaps are faster for retrieval compared to Treemap.
Retrieval in Treemap is slower as it uses tree traversal to find keys.
Hashmap is implemented by using an Array of linked list.
TreeMap is implemented using a Red-black Tree.
Hashmap uses the equals() method of the Object class to compare keys.
TreeMap uses compareTo() method to compare keys.
The queue is a linear Data structure that is used to store a collection of elements.
Deque also known as a Double-ended queue is also a linear data structure that stores a collection of elements with operations to remove and add from both ends.
Elements in the queue can only be inserted at the end of the data structure.
Elements can be inserted from both ends of the data structure.
Queue can be implemented using Array or Linked List.
Dequeue can be implemented using Circular Array or Doubly Linked List.
Queues are generally used to implement a waiting list or task queue.
Deque is used to implement a stack or dequeuing elements from both ends.


HashSet is unordered.
TreeSet is based on natural ordering.
HashSet allows null elements.
TreeSet does not allow null elements.
HashSet is Implemented by the HashSet class.
TreeSet is Implemented by TreeSet class.
HashSet hs = new HashSet<>();
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet<>();

According to various resources, The average salary of a Java Backend Developer is more than 14 lakhs per annum which is 30% higher than any other developer role . Here you can also check our latest course on Java Backend Development !
A Java developer writes code, designs software solutions, and builds applications using the Java programming language. They collaborate with teams, solve problems, and ensure code quality for efficient and reliable software development.
A Java developer should have a strong understanding of core Java concepts such as object-oriented programming, data types, control structures, and exception handling. Additionally, knowledge of frameworks like Spring, Hibernate, and web development technologies like Servlets and JSP is beneficial. Other than Technical Skills Problem-solving, debugging, and critical thinking skills are also highly valued.
To prepare for a Java interview, start by reviewing fundamental Java concepts and practice coding exercises. Study common interview questions related to core Java, data structures, algorithms, and multithreading from GeeksforGeeks Interview Section . Additionally, brush up on design patterns, database connectivity, and web development frameworks. Practising coding challenges on platforms like GeekforGeeks Practice Portal can also be helpful.
To stand out in a Java interview, demonstrate a deep understanding of Java concepts and practical applications. Showcase your problem-solving skills by explaining your approach to complex scenarios and providing efficient solutions. Additionally, highlight any relevant projects or contributions you’ve made to the Java community. Showing enthusiasm, good communication, and a willingness to learn can also leave a positive impression.